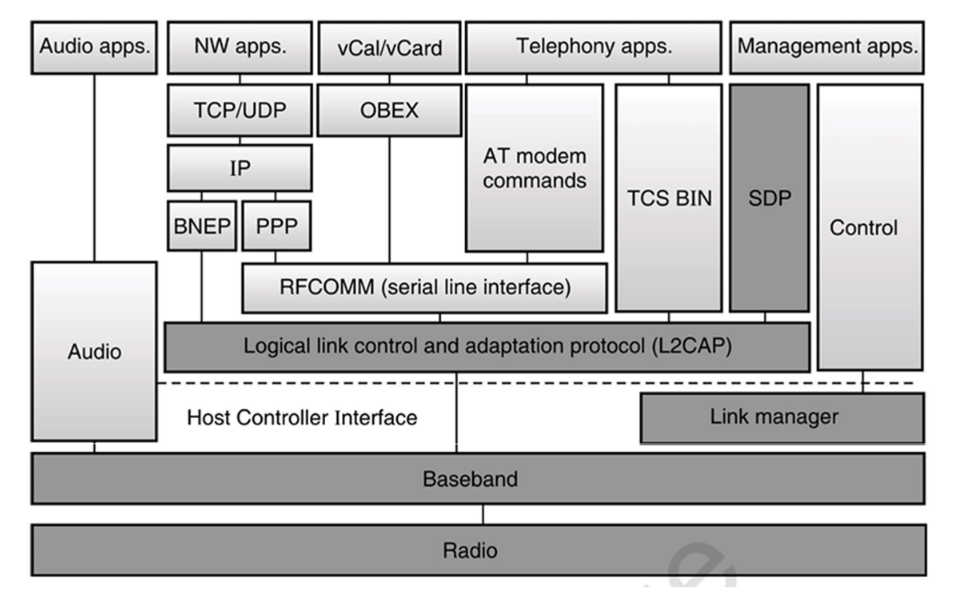
Bluetooth Stack Overview
The Bluetooth stack is divided into three main sections:
-
Application Layer
-
Host Stack (Software Protocols)
-
Controller Stack (Firmware/Hardware)
1. Application Layer
This is where user-level applications operate. Examples include:
-
Audio Applications – For streaming music.
-
Network (NW) Applications – For sharing internet connections.
-
Telephony Applications – For managing voice calls.
-
vCal/vCard Applications – For sharing calendar events and contacts.
-
Management Applications – For controlling and managing Bluetooth services and settings.
2. Host Stack (Software Protocols)
These protocols enable communication between the application layer and the controller:
-
L2CAP (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol)
-
Adapts different application needs to the Bluetooth baseband.
-
Most upper-layer protocols pass through L2CAP.
-
-
RFCOMM (Radio Frequency Communication)
-
Emulates serial cable communication.
-
Commonly used in profiles like file transfer and headsets.
-
-
SDP (Service Discovery Protocol)
- Enables Bluetooth devices to discover services offered by other devices (e.g., file sharing support).
-
BNEP (Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol)
-
Used for sending Ethernet packets.
-
Supports Personal Area Networking (PAN).
-
-
OBEX (Object Exchange Protocol)
- Facilitates file transfers and object exchange.
-
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
- Supports dial-up networking over Bluetooth.
-
TCS BIN & AT Commands
-
TCS BIN: Manages call control in telephony.
-
AT Commands: Used to control modems (e.g., in headsets and phones).
-
-
Audio
- Sends audio streams directly to the controller, bypassing L2CAP.
-
Control
- Handles management tasks like pairing, role switching, and device configuration.
3. Controller Stack (Firmware/Hardware)
Responsible for low-level communication and transmission:
-
Host Controller Interface (HCI)
-
Acts as the interface between the Host Stack and Controller Stack.
-
Transports commands, data, and events.
-
-
Link Manager
- Manages link setup, authentication, encryption, and Quality of Service (QoS) negotiation.
-
Baseband
-
Handles packet conversion for wireless transmission.
-
Includes functions like error correction and flow control.
-
-
Radio
- The physical transmitter and receiver operating in the 2.4 GHz ISM band.