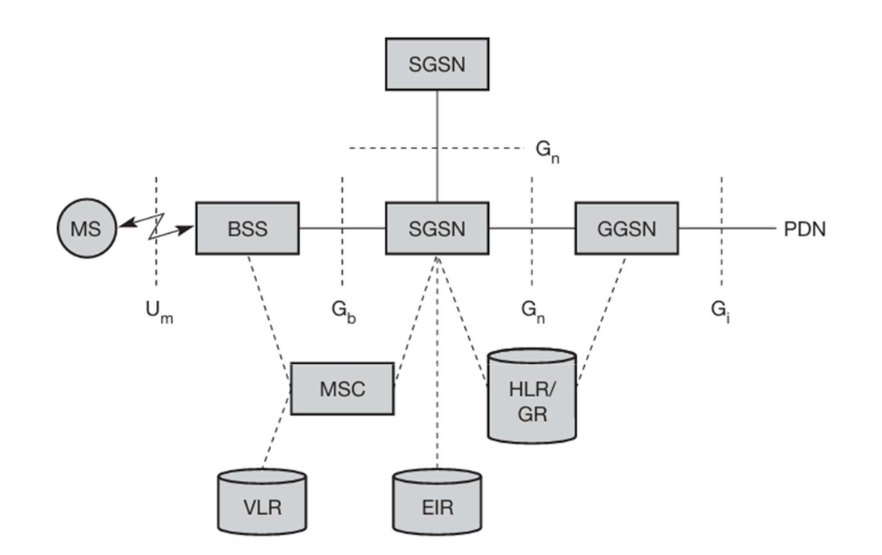
Introduction to GPRS Architecture
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a packet-oriented mobile data service that enhances GSM networks by enabling efficient, always-on Internet connectivity and data transmission. Unlike traditional circuit-switched GSM services, GPRS allows for packet switching, which improves bandwidth utilization and supports data applications such as web browsing, email, and multimedia messaging.
GPRS Architecture Components
1. Mobile Station (MS)
-
The user’s mobile device (phone, tablet).
-
Communicates with the network using the Um interface (radio link).
2. Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
-
Includes Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC).
-
Handles radio communication with the MS.
-
Uses the Gb interface to connect to the SGSN.
3. Mobile Switching Centre (MSC)
-
Handles traditional voice calls, SMS, and circuit-switched services.
-
Works alongside SGSN to provide integrated voice and data services.
4. Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN)
-
Manages packet-switched data services for mobile users.
-
Responsible for mobility management, authentication, and data packet forwarding.
-
Interfaces with:
-
VLR (Visitor Location Register): Stores temporary subscriber data.
-
EIR (Equipment Identity Register): Validates the device identity.
-
HLR/GR (Home Location Register/Gateway Register): Maintains subscriber profiles and service data.
-
5. Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
-
Acts as an interface between the GPRS network and external packet data networks (e.g., the Internet or corporate networks).
-
Assigns IP addresses to mobile users.
-
Uses the Gi interface to connect to Public Data Networks (PDNs) and the Gn interface to communicate with SGSNs.
6. Public Data Network (PDN)
-
External IP-based networks such as the Internet or corporate intranets.
-
The GGSN facilitates data exchange between the PDN and mobile subscribers.
Key Interfaces in GPRS Architecture
-
Um: The wireless radio interface between the Mobile Station (MS) and the Base Station Subsystem (BSS).
-
Gb: Connects the BSS to the SGSN for packet data transmission.
-
Gn: Connects SGSNs and GGSNs within the GPRS core network for packet routing.
-
Gi: Connects the GGSN to external Public Data Networks (PDNs), such as the Internet.