When a mobile user is engaged in conversation, the MS (Mobile Station) is connected to the BTS (Base Transceiver Station) via radio link. If the mobile user moves to the coverage area of another BTS, the radio link to the old BTS is eventually disconnected, and a radio link to the new BTS is established to continue the conversation. This process is called handover or handoff.
There are four types of handovers in GSM
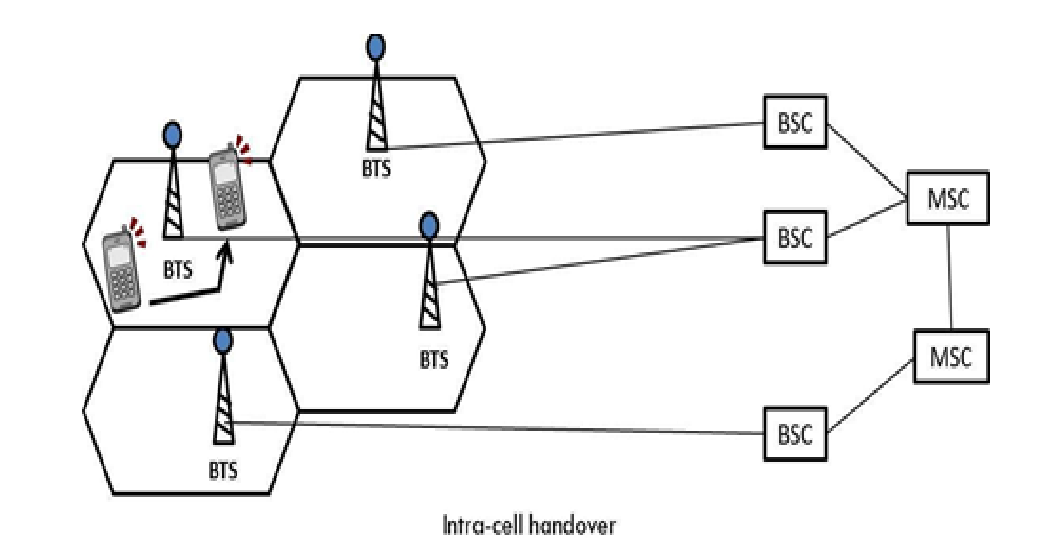
1. Intra-Cell Handover
- Occurs within the same cell but between different frequency channels or time slots.
- Used to reduce interference or improve signal quality.
- Example: A call remains in the same base station but switches to a different frequency
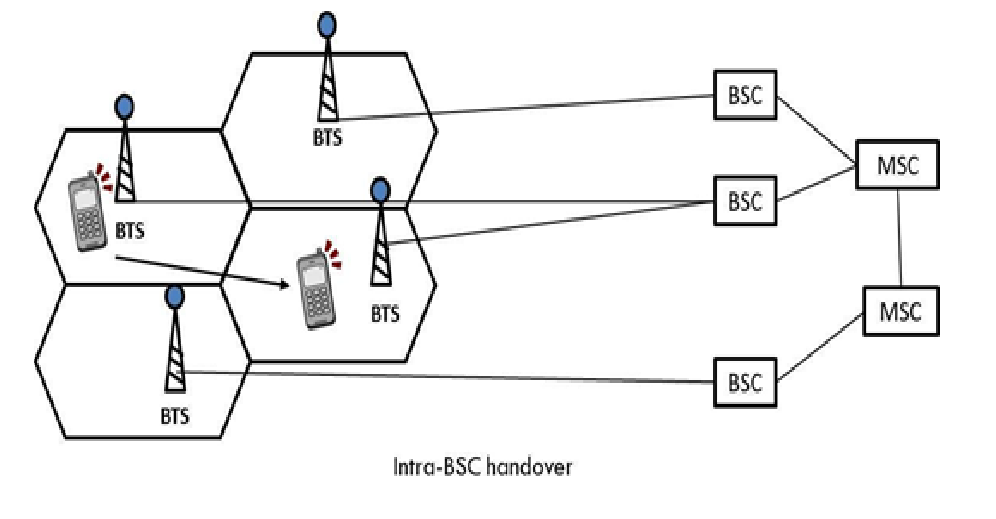
2. Inter-Cell Handover (Intra-BSC Handover)
- Occurs between two cells controlled by the same Base Station Controller (BSC).
- The Mobile Station (MS) moves from one Base Transceiver Station (BTS) to another, but the BSC remains unchanged.
- Example: A user moving from one cell to another within the same city under the same BSC.
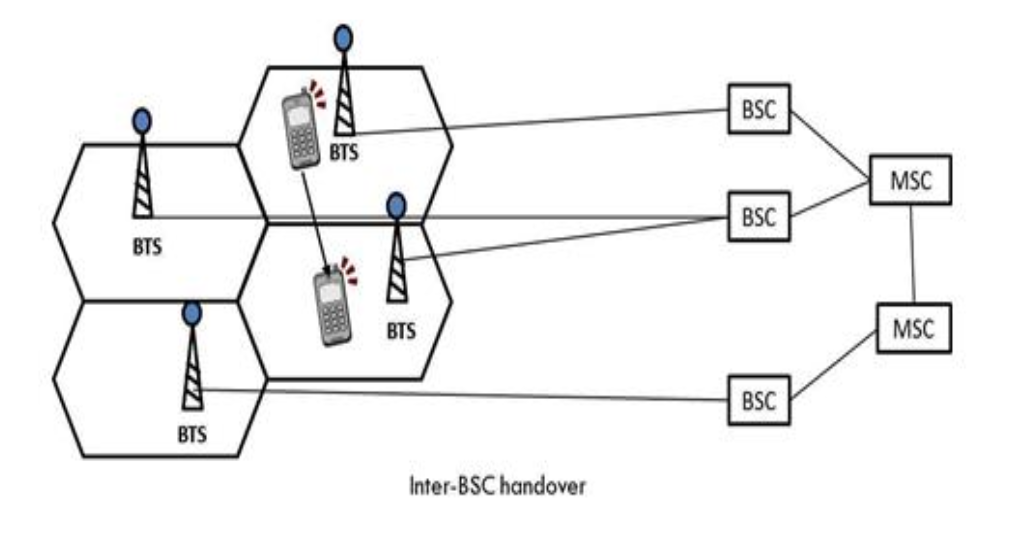
3. Inter-BSC Handover
- Happens when a call is transferred between two different BSCs but within the same Mobile Switching Centre (MSC).
- The MSC manages the handover process to ensure a smooth transition.
- Example: A user moves from one city area to another, and the call is handled by a different BSC.
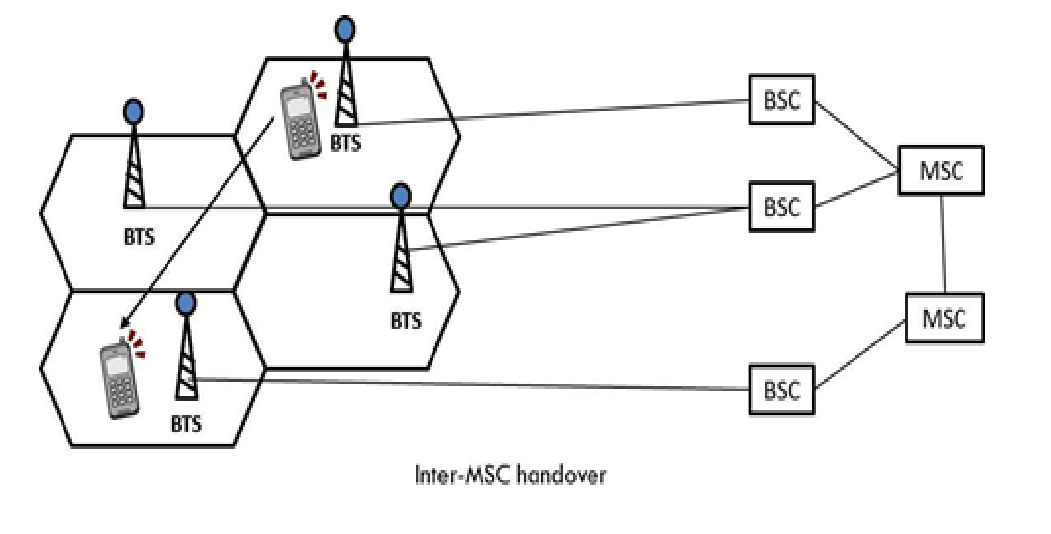
4. Inter-MSC Handover
- Occurs when the mobile user moves between two different MSCs.
- Requires coordination between the two MSCs to transfer the call.
- Example: A person traveling between different states or large regions.