Overview
GSM uses several cryptographic algorithms to ensure authentication, confidentiality, and privacy of the communication between a mobile station (MS) and the network.
The key algorithms are:
-
A3 — used for authentication
-
A8 — used for generating the session key
-
A5 — used for encrypting the communication (privacy)
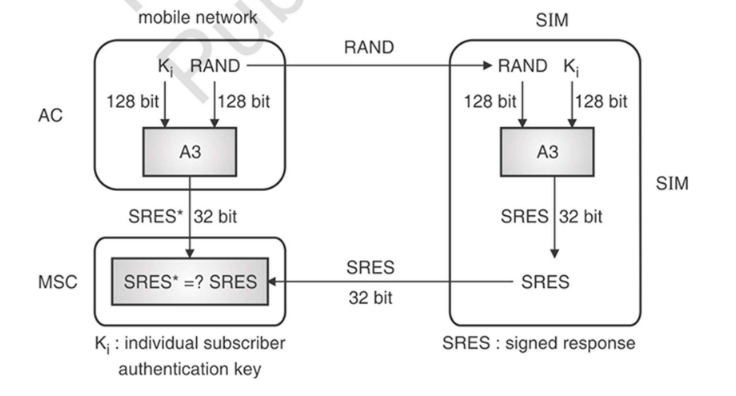
1. A3 Algorithm (Authentication)
-
Purpose: Verify the identity of the mobile subscriber to the network.
-
How it works:
-
The SIM card and the network both share a secret key called Ki (individual subscriber authentication key).
-
When the MS tries to connect, the network sends a random challenge number called RAND.
-
The SIM applies the A3 algorithm to RAND and Ki, producing a Signed Response (SRES).
-
The MS sends the SRES back to the network.
-
The network computes the expected SRES using its copy of Ki and RAND.
-
If the two SRES values match, the subscriber is authenticated.
-
-
Example implementation: The most widely used A3 algorithm is COMP128.
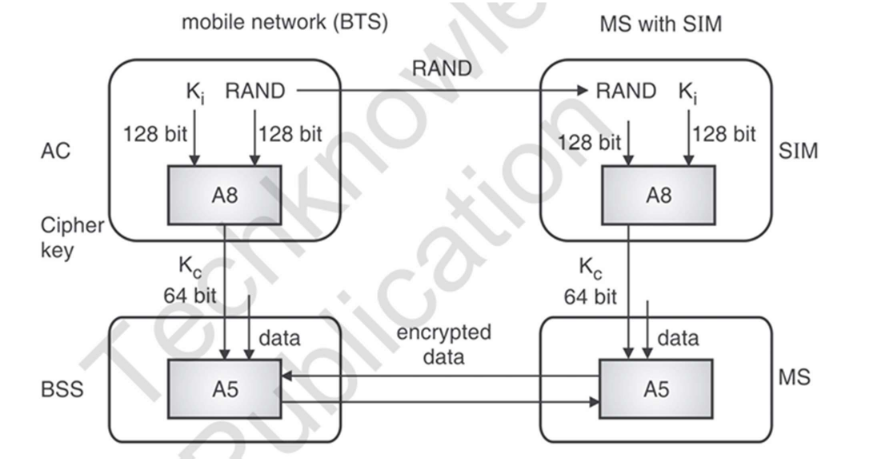
2. A8 Algorithm (Session Key Generation)
-
Purpose: Generate the ciphering key used to encrypt the communication.
-
How it works:
-
Like A3, it takes the Ki and the same RAND as inputs.
-
It outputs a 64-bit session key (Kc).
-
This session key Kc is used for encrypting/decrypting the over-the-air data.
-
Typically, A3 and A8 are implemented together in COMP128, so they run simultaneously with the same inputs.
-
3. A5 Algorithm (Encryption/Privacy)
-
Purpose: Encrypt the actual communication between MS and base station to protect confidentiality.
-
How it works:
-
Uses the session key Kc generated by A8.
-
Encrypts the voice and data over the air interface using a stream cipher.
-
There are different versions of A5 with varying strength:
-
A5/1: Stronger encryption, used mainly in Europe.
-
A5/2: Weaker encryption, used in some countries due to export restrictions.
-
A5/3: A newer, stronger encryption algorithm based on Kasumi block cipher.
-
-
-
Encryption ensures that anyone eavesdropping cannot easily understand the transmitted data.