Overview
Snooping TCP is a TCP-aware link-layer protocol employed in wireless networks to enhance TCP performance over unreliable wireless links. It is implemented at the base station, where it monitors TCP packets (both data and acknowledgments) that pass through it. Traditional TCP interprets all losses as congestion, leading to unnecessary retransmissions and reduced performance. Snooping TCP helps mitigate this by handling retransmissions locally without unnecessarily involving the sender.
Working Mechanism:
The mobile host communicates with a correspondent host via a foreign agent (such as a base station or router). The TCP connection is end-to-end between the mobile host and the correspondent host. The foreign agent “snoops” or monitors TCP ACKs from the mobile host and buffers TCP data packets sent from the correspondent host to the mobile host. If an ACK is not received within a certain time (indicating possible loss), the foreign agent locally retransmits the buffered data to the mobile host without involving the sender.
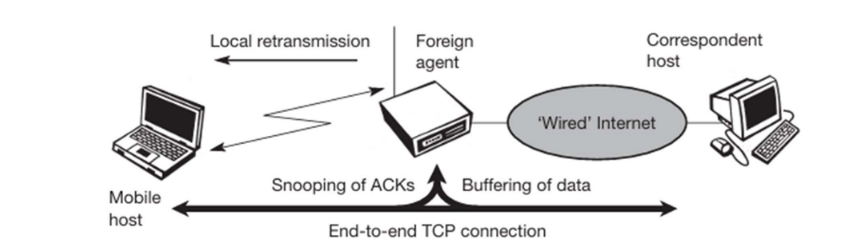
Advantages of Snooping TCP:
-
Maintains End-to-End Semantics: The end-to-end TCP connection remains intact.
-
Local Recovery: Wireless link errors are corrected quickly by the base station without involving the sender.
-
Improved Throughput: Avoids unnecessary reduction of TCP window size, maintaining better flow.
-
Automatic Fallback: The approach automatically falls back to standard TCP if the enhancements stop working.
-
No Correspondent Host Changes: The correspondent host does not need to be changed, as most enhancements are in the foreign agent.
-
No Mobile Host Changes (for one direction): Supporting only the packet stream from the correspondent host to the mobile host does not require changes in the mobile host.
Disadvantages of Snooping TCP:
-
Not Fully Transparent: Requires additional support like Negative Acknowledgments (NACK) at the mobile host, which can break transparency.
-
Wireless Link Dependency: Performance is dependent on the wireless link; delays may trigger unnecessary retransmissions.
-
Ineffective with Encryption: Encrypted TCP headers prevent snooping, rendering Snooping TCP ineffective.