Types of Antennas and Their Radiation Patterns
Antennas are crucial components in wireless communication, converting electrical signals into electromagnetic waves (transmission) and vice versa (reception). Their radiation patterns define how energy is distributed in space. Below are the key types of antennas and their radiation characteristics:
1. Isotropic Antenna
- Radiation Pattern: Spherical (uniform in all directions).
- Description:
- Hypothetical antenna used as a reference for comparison.
- Radiates equally in all directions (360° in 3D space).
- Real-world equivalent: Omnidirectional antennas approximate this pattern in 2D (horizontal plane).

2. Dipole Antenna
- Radiation Pattern:
- 2D (Horizontal): (bidirectional).
- 3D: Torus/donut-shaped (nulls at the ends).
- Description:
- Simplest practical antenna (e.g., half-wave dipole).
- Consists of two conductive elements.
- Used in FM radio, TV antennas, and RFID.

3. Directional Antenna
- Radiation Pattern: Concentrated beam (unidirectional).
- Examples:
- Yagi-Uda Antenna: High gain, used in TV reception.
- Parabolic Reflector: Focuses signals into a narrow beam (satellite dishes).
- Applications: Point-to-point communication (e.g., radar, satellite links).
4. Omnidirectional Antenna
- Radiation Pattern:
- Horizontal Plane: 360° coverage (circular).
- Vertical Plane: Reduced coverage above/below the antenna (donut-shaped).
- Examples:
- Monopole Antenna (e.g., car antennas).
- Whip Antenna (mobile base stations).
- Applications: WiFi routers, FM broadcasting.

5. Sectorized Antenna
- Radiation Pattern: Pie-shaped (e.g., 120° or 60° sectors).
- Description:
- Used in cellular networks (e.g., 4G/5G base stations).
- Combines directional focus with multi-sector coverage.
- Advantage: Increases capacity by reducing interference between sectors.
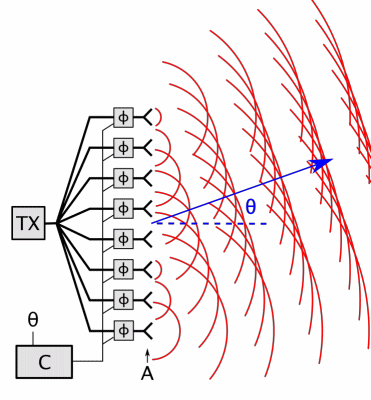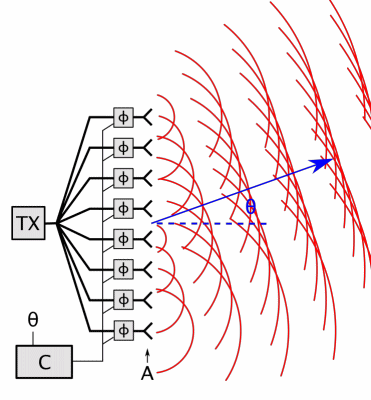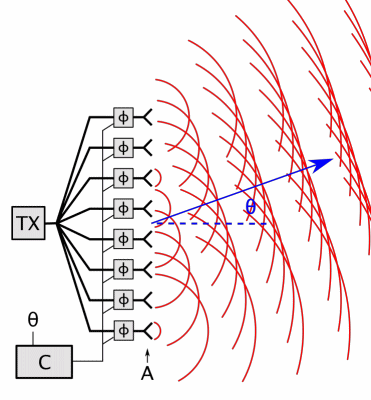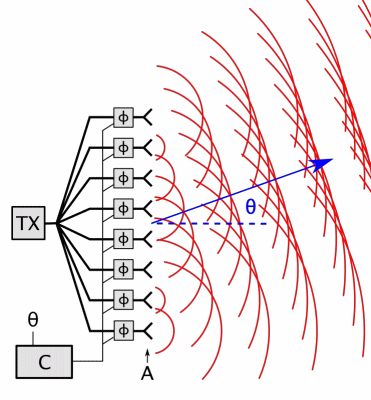
6. Array Antenna
- Radiation Pattern: Controllable (steerable beams or high gain).
- Types:
- Phased Arrays: Electronically steer beams (used in 5G, military radar).
- MIMO Arrays: Multiple inputs/outputs for spatial multiplexing (LTE/5G).
- Applications: Satellite communication, beamforming in 5G.
Summary Table
| Antenna Type | Radiation Pattern | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Isotropic (Theoretical) | Spherical (uniform) | Reference for gain calculations |
| Dipole | Figure-8 (bidirectional) | FM radio, RFID |
| Directional | Narrow beam (unidirectional) | Satellite, radar, point-to-point |
| Omnidirectional | 360° (horizontal) | WiFi, mobile base stations |
| Sectorized | Pie-shaped (e.g., 120°) | Cellular networks (4G/5G) |
| Array | Steerable beams | 5G, MIMO, military radar |