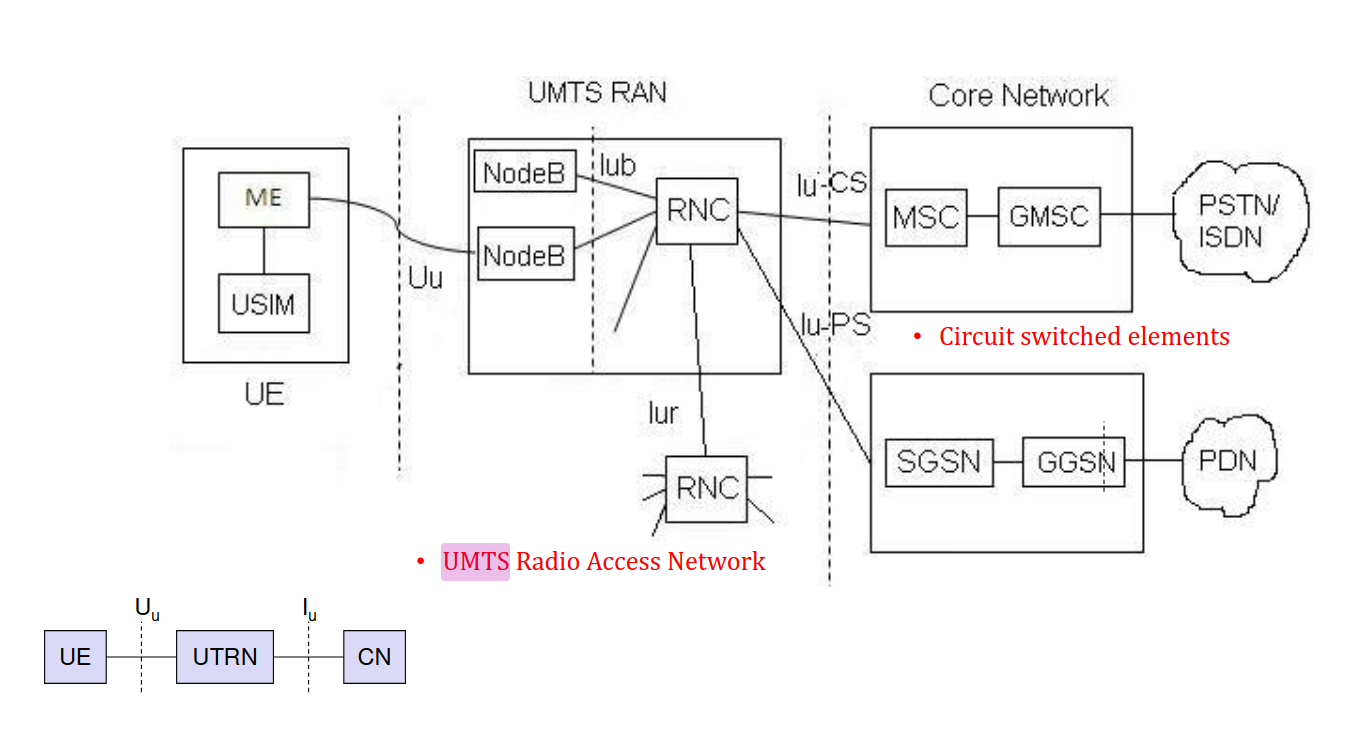
UMTS Architecture (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System)
UMTS is a 3rd Generation (3G) mobile communication system that enhances GSM by offering higher data rates, multimedia services, and improved capacity. It is based on a new radio access technology (W-CDMA) and integrates with the existing GSM core.
Main Components of UMTS Architecture
UMTS architecture consists of three main domains:
1. User Equipment (UE)
-
The mobile device used by the subscriber.
-
Components:
-
ME (Mobile Equipment) – the hardware (phone).
-
USIM (Universal Subscriber Identity Module) – stores subscriber identity, authentication keys, etc.
-
2. UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN)
-
Responsible for the radio access part.
-
Components:
-
Node B: Equivalent to BTS in GSM; handles radio transmission/reception.
-
Radio Network Controller (RNC):
-
Manages multiple Node Bs.
-
Handles handover, radio resource management, encryption, etc.
-
-
3. Core Network (CN)
-
Responsible for switching, routing, and service control.
-
Divided into two domains:
a) Circuit-Switched Domain
-
Handles voice calls.
-
Components:
-
Mobile Switching Centre (MSC)
-
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
-
Gateway MSC (GMSC)
-
b) Packet-Switched Domain
-
Handles data services like internet.
-
Components:
-
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN)
-
Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
-
Interfaces
| Interface | Between | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Uu | UE ↔ Node B | Radio interface using W-CDMA |
| Iub | Node B ↔ RNC | Controls radio resources, transport bearer info |
| Iur | RNC ↔ RNC | Supports inter-RNC handover |
| Iu-CS | RNC ↔ MSC (CS Domain) | Circuit-switched services |
| Iu-PS | RNC ↔ SGSN (PS Domain) | Packet-switched services |
Key Features of UMTS:
-
Supports up to 2 Mbps data rate.
-
Uses W-CDMA for radio access.
-
Offers global roaming and multimedia services.
-
Separates circuit and packet switching, enabling better data/voice integration.